Waste Management 2019
About Conference
ABOUT CONFERENCE
The Euroscicon is inviting for 6th Edition of European Conference on Water, Waste and Energy Management on May 13 - 14, 2019 at Stockholm, Sweden. The point of the ebb and flow year's social affair is Advocating Water, Waste and Energy for Clean and Green Environment which will give an overall stage to discuss present and the fate of Water, Waste and Energy Management. The augmentation of three submitted streams for the European Conference on Water, Waste and Energy Management get-together will be a hit, we could get gaining from two particular get-together one that outperformed wants in the ponder and gathering end and one that outperformed wants in the business and key end. The 2019 foundation of this gathering will empower us to continue plunging further into both the examination of Environmental change and the business necessities for associations.
The Organizing Committee is fulfilled to welcome you to go to the 6th Edition of European Conference on Water, Waste and Energy Management, one of its shocking Environmental and its related field of social affairs to be held amidst on May 13-14, 2019 in Stockholm, Sweden. European Conference on Water, Waste and Energy Management joins researchers, specialists and CROs from around the globe. The thought process of this meeting is to advance the exponential change of our Environment over a coming couple of years. Different unsafe things are influencing nature and accordingly, the administration is required with the goal that our future age could likewise take recreation of our spotless and green Environment.
At Water, Waste and Energy Management meet your arranged interest packs from around the globe concentrated on finding a few solutions concerning Water, Waste and Energy administration. This get-together would be your single most clear chance to achieve the best aggregation of people the world over a social event to chat on a critical worry of this period.
Why to Attend?
Join your colleagues around the globe concentrated on finding a few solutions concerning Water, Waste and Energy Management related advances, which is your single most evident chance to achieve the best assembling of people from the Water, Waste and Energy Management societies, arrange appears, dissipate data, meet with repeating example and potential masters, make a sprinkle with new research works, and get name certification at this Two-day occasion. Comprehensively acclaimed speakers, the latest research, moves, and the most energy revival in Environment are signs of this social affair. The arrangement of data on new advances actualized in the field of Water, Waste and Energy Management and a sound learning on the Global Warming will give collaboration the world's outstanding Professors, CEOs.
Benefits to attend Water, Waste and Energy Management:
a) Keynote introduction alongside connections to excite established researchers.
b) Workshop and symposiums to accomplish the greatest cluster of individuals from the Environmental Science society.
c) A wide track of exhibitors to grandstand the new and rising advancements.
d) Platform to worldwide speculation group to interface with partners in Environment/Civil Engineers area.
e) Links to the political promoting assets remembering the ultimate objective to expand your business and researches.
f) Triumph of Awards, Certificates perceives your sense of duty regarding your calling to empower the incipient research.
Water, Waste and Energy Management Benefits:
• Open board exchanges: Providing an open gathering with specialists from the scholarly world and business to talk about on current difficulties in Water, Waste and Energy Management, where all participants can collaborate with the board took after by a Q&A session.
• Speaker and notice introductions: Providing a stage to all academicians and industry experts to share their exploration contemplations and discoveries through a discourse or a publication introduction.
• Editorial executive gathering: Discussing on development and advancement of management techniques for water, waste and energy. Open access to International Journals and enlisting board individuals and analysts who can bolster the diary.
• Roundtable gatherings: Providing a stage where industry experts meet scholastic specialists.
Business and Exhibitor Benefits:
Over 50+ organizations and international pavilions will be exhibiting at the European Conference of Water, Waste and Energy Management. Exhibitors will include equipment manufacturers and suppliers, systems providers, finance and investment firms, R&D Companies, project developers, trade associations, and government agencies.
In addition to the products and services, you will have access to valuable content, including Keynote Presentations, Product Demonstrations and Educational Sessions from today’s industry leaders.
The 6th Edition of European Conference on Water, Waste and Energy has everything you need, all under one roof, saving you both time and money. It is the event you cannot afford to miss!
Target Audience:
- Executives, CEO's of Organizations
- Business Development Managers
- Boss Scientific Officers
- Research and development Researchers from Water, Waste and Energy Management
- Industries.
- Educators, Associate Professors, Assistant Professors
- Ph.D. Scholars
- Patent Attorneys
- Protected innovation Attorneys
- Speculation Analysts
- Affiliation, Association presidents, and experts
- Environmental journalists
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) inspectors
- Environmental Compliance Agency workers
- Interpretive naturalists
- Environmental advocates
- Technical writers
- Organizers
- Lobbyists
- Water and air quality engineers
- Civil Engineers
- Solid and hazardous waste engineers
- Pollution control technicians
- Wastewater treatment plant operators
- Programming improvement organizations
- Research Institutes and individuals
- Inventory network organizations
- Assembling Companies
- CRO (Contract Research Organization) and DATA administration Companies
- Preparing Institutes
- Business Entrepreneurs
About Venue:
Stockholm, the capital of Sweden, encompasses 14 islands and more than 50 bridges on an extensive Baltic Sea archipelago. The cobblestone streets and ochre-colored buildings of Gamla Stan (the old town) are home to the 13th-century Storkyrkan Cathedral, the Kungliga Slottet Royal Palace, and the Nobel Museum, which focuses on the Nobel Prize. Ferries and sightseeing boats shuttle passengers between the islands.
Stockholm is also the cultural, media, a political and economic centre of Sweden. The Stockholm region alone accounts for over a third of the country's GDP and is among the top 10 regions in Europe by GDP per capita. It is an important global city and the main centre for corporate headquarters in the Nordic region. The city is home to some of Europe's top ranking universities, such as the Stockholm School of Economics, Karolinska Institute and Royal Institute of Technology (KTH). It hosts the annual Nobel Prize ceremonies and banquet at the Stockholm Concert Hall and Stockholm City Hall. One of the city's most prized museums, the Vasa Museum, is the most visited non-art museum in Scandinavia. The Stockholm metro, opened in 1950, is well known for the decor of its stations; it has been called the longest art gallery in the world. Sweden's national football arena is located north of the city centre, in Solana. Ericsson Globe, the national indoor arena, is in the southern part of the city. The city was the host of the 1912 Summer Olympics and hosted the equestrian portion of the 1956 Summer Olympics otherwise held in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
Scientific Sessions
Track 1-Climate Change:

Climate change is a change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns that lasts for an extended period of time. The Earth's climate has been changing throughout the history. Just in the last 650,000 years there have been seven cycles of glacial advance and retreat, with the abrupt end of the last ice age about 7,000 years ago marking the beginning of the modern climate era and of human civilization. Most of these climate changes are attributed to very small variations in Earth’s orbit that change the amount of solar energy our planet receives. At present, the current scenario of the climate change is at alarming levels. The present warming trend is of particular significance because most of it is very likely human-induced and proceeding at a rate that is unprecedented in the past 1,300 years. Earth-orbiting satellites and other technological advances have enabled scientists to see the big picture, collecting many different types of information about our planet and its climate on a global scale. This body of data, collected over many years, reveals the signals of a changing climate.
Regardless of international climate protection commitments, greenhouse gasoline emissions endured to upward push global inside the beyond a year, accomplishing new report highs. That is one of the key findings of the country of the weather 2017 record, which has now been published by means of America national Oceanic and Atmospheric administration (NOAA). The report, wherein greater than 500 researchers from sixty five nations have worked, files climate phenomena and developments within the worldwide weather. The 12 months 2017 ranked most of the 3 warmest years on account that the beginning of the cutting-edge climate record in 1880. Global it becomes characterized by way of rising temperatures, coral dying within the oceans, melting glaciers, withdrawing sea ice and growing sea degrees.
- Climate Change & Climatology
- Evidence of Climate Changes
- Biodiversity Scenarios
- Carbon Cycle
- CO2 Capture and Sequestration
- Climate Hazards
- Risks of Climate Change
- Energy Policy
Track 2-Nuclear Energy:

Atomic power is the utilization of atomic responses that discharge atomic vitality to create warm, which most oftentimes is then utilized as a part of steam turbines to deliver power in an atomic power plant. The term incorporates atomic parting, atomic rot, and atomic combination. Nuclear technology uses the energy released by splitting the atoms of certain elements. It was first developed in the 1940s, and during the Second World War research initially focused on producing bombs. In the 1950s attention turned to the peaceful use of nuclear fission, controlling it for power generation.
The global nuclear energy demand exceeded 2,400 TWh in 2014 and it is estimated to grow at a CAGR of over 4% from 2015 to 2022. Nuclear energy accounted over 11% of the global energy generation in 2014. Increasing power and energy demand from households and industrial sectors is expected to fuel market growth over the forecast period.
Rapid population growth along with improved lifestyle has resulted in an augmented energy demand from households. Rising demand for a variety of products has driven industrial developments in various countries, thus increasing energy requirements from manufacturing sector. As of 2014, nuclear power provides over 11% of the world's electricity, and over 21% of the electricity in OECD countries.
- Problems with Nuclear Power
- Capabilities of Nuclear Power
- Nuclear Power Plants
- Life Cycle of Nuclear Fuel
- Nuclear Proliferation
- Environmental Issues
Track 3 Fossil fuels:

Fossil fuel, any of a class of hydrocarbon-containing materials of biological origin occurring within Earth’s crust that can be used as a source of energy. All fossil fuels can be burned in air or with oxygen derived from air to provide heat. This heat may be employed directly, as in the case of home furnaces, or used to produce steam to drive generators that can supply electricity.
The twentieth century noticed a big diversification of fossil strength consumption, with coal declining from ninety-six percentage of overall production in 1900 to less than 30 percent in 2000. Today, crude oil is the biggest power supply, accounting for round 39 percentage of fossil energy, accompanied with the aid of coal and natural fuel at 33 and 28 percent, respectively.
- Coal Mining
- Petroleum Production
- Oil
- Coal
- Natural Gas
Track 4-E –waste:

The composition of e-waste is diverse, containing more than 1,000 different toxic and non-toxic substances. The onset of technological advancement of electrical and electronic appliances is so rapid that new products quickly replace existing models or make certain items of electronic equipment redundant, useless, thereby generating a constant source of e-waste generation. E-waste is created from all electronic: computers, TVs, monitors, cell phones, PDAs, VCRs, CD players, fax machines, printers and many more.
Global E-Waste control market is anticipated to garner $49.4 billion through 2020, registering a CAGR of 23.5% at some stage in the forecast length 2014 - 2020. It's far one of the quickest developing waste streams in emerging as well as evolved areas. The decreased existence spans of electrical, digital and customer digital devices are producing huge E-Waste, which is growing swiftly every 12 months.
- Medical devices
- Plastic Pollution
- Toxic Waste
- Land Pollution
- Motion-Picture Technology
Track 5-Environmental Chemistry:
Environmental chemistry is the study of chemical and biochemical processes occurring in nature. These impacts may be felt on a local scale, through the presence of urban air pollutants or toxic substances arising from a waste site, or on a global scale, through depletion of stratospheric ozone or global warming. However, it is important to realize that all forms of matter in our environment whether synthetic or natural are made of chemicals.
The global Environment chemistry marketplace length becomes worth USD 1,023.7 million in 2016, growing at a CAGR of nine.9% over the forecast duration, increasing penetration of the generation in pharmaceuticals region is expected to be the fundamental riding component over the forecast period. It is taken into consideration the green era because of its surroundings-friendly nature and advanced houses in comparison to the batch production tactics.
- Environmental Pollution
- Atmospheric Pollution
- Regional Air Pollution
- Acid Rain
- Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
- Climate Change
- Water Pollution
- Soil Pollution
Track 6-Reduce, Reuse, Recycle and Recovery:

Reduce: this entails the deliberate lowering of the number of plastics an individual uses in their day to day life. Reuse: this involves putting to use plastics that have already been used. This can mean putting them to better use than just throwing them away. Recycle: The basic phases in recycling are the collection of waste materials, their processing or manufacture into new products, and the purchase of those products, which may then themselves be recycled. Recycling can help reduce the quantities of solid waste deposited in landfills, which have become increasingly expensive. Recovery: this entails the insistence on not using plastic but rather finding and using existing alternatives.
Manufacturing products from recycled materials consume less energy and produce less pollution than producing the same items from virgin materials. Reducing our use of virgin materials conserves natural resources like trees, water and minerals.
The global marketplace revenue is probably to increase from $265.61 billion in 2017 to $282.1 billion in 2018. This doesn't include the revenue from plastic recycling enterprise, which itself poses an awesome commercial enterprise possibility and the market length is envisioned at $37.6 billion in 2018, a large boom of 7.1% from 2017.
- Waste Disposal
- Reduce
- Recycle
- Reuse
- Recovery
Track 7-Waste and Biomass Valorization:

Waste and Biomass Valorization is the process of treatment of waste for (landfill) disposal, storage, and in some cases sorting. In the 1990s, depletion of raw materials and socio-economic concerns supported the direct recycling of waste and residues. Various valorization techniques are currently showing promise in meeting industrial demands. Waste and Biomass Valorization is the process of treatment of waste for (landfill) disposal, storage, and in some cases sorting. Various valorization techniques are currently showing promise in meeting industrial demands. Due to depletion of natural resources, increasing greenhouse emissions and awareness of the need for sustainable development in terms of safely reusing waste and biomass, the transformation of waste/biomass to valuable materials and energy is emerging as a strong trend.
A number of exciting fee chains has been diagnosed. specifically, waste from rice, maize, sugar cane, coffee, tea and residual streams from breweries may be valorized to bio-primarily based products for which there is a marketplace, e.g. plastic packaging substances, seedling tubes and kitchen utensils, chemical compounds, and energy. Most business price can be accomplished whilst distinct residual flows can be blended into a mess of merchandise, which emphasizes the significance of Biomass Valorization middle in Rwanda. Here, partners can alternate applicable knowledge, take a look at technological standards in a nearby context and analyze both technical in addition to commercial feasibility.
- Trends in Syngas
- Non-Virgin Biomass
- Biomass Valorization in Phytomedicine
- Harnessing Agro-Wastes for Bioethanol Production
- Blended Biomass
Track 8-Solid Waste Management:

Solid waste management refers to all activities pertaining to the control of generation, storage, collection, transfer, and transport, treatment and processing, and disposal of solid wastes in accordance with the best principles of public health, economics, engineering, conservation, aesthetic, and other environmental consideration.
The Global Waste management marketplace becomes valued at $285.zero billion in 2016 and is anticipated to attain $435.zero billion via 2023. Waste control is the process of treating solid wastes. It offers one of kind answers to recycle items that don’t belong to trash. It includes activities that assist control waste from its inception to very last disposal. This consists of the collection, shipping, remedy, and disposal of waste at the side of inspection and law.
- Combustible solid wastes
- Plasma Arc Gasification
- Hazardous-Waste Management
- Sewerage System
- Emissions Trading
Track 9-Renewable Resources:

Renewable resources can be described as a rather tricky balancing act. Renewable resource intake and use commonly do not yield decomposition or contribute to global warming. It is easy to recognize the environmental advantages of utilizing the alternative and renewable forms of energy but we must also be aware of the disadvantages. It can be crucial to develop the capacity of electricity that is as large as those produced by traditional fossil fuel generators.
The worldwide strength sector improved the production of primary electricity from 5.5 Btoe in 1970 to nearly 13.eight Btoe in 2015. The installed capacity for electricity era reached 6.2 billion KW in the year 2015 and the Asia Pacific received relevance, currently representing forty-six % of that potential. Coal, oil and other fossil fuels nonetheless constitute a considerable proportion of the matrix, with renewable resources representing best 19.2% of intake.
- Solar Energy
- Hydroelectricity
- Bio Renewable Chemicals
- Natural Resource
- Geothermal Energy
Track 10-Mine Waste & Tailing:
A feasibility study of a wearable helmet in order to protect mine workers especially of goldmines from carbon monoxide poisoning and cyanidation. Carbon monoxide poisoning is a common problem faced by the workers of coal, gold and many other mines. On the other hand cyanidation problem occurs in gold mines only during ore processing. Current safety systems for mine workers, only monitors environmental concentrations of gas. This is insufficient because toxic exposures effects people at different levels based on their immunity levels. During mining process CO can be emitted which is an odourless gas and lighter than air, it cannot be sensed by workers and effects the haemoglobin range in the body so a CO gas sensor is implemented here in order to detect CO, if the density of CO exceeds inside the mines then the exhaust fan can be switched ON automatically. Recent research on environmental and social risks and business costs in the extractive industry found that environmental issues were the most common cause of disputes, resulting in lost productivity. International best practices and compliance standards have set the benchmark for mining companies together with national legislation.
The mining waste management market is estimated to be 173.64 billion tons in 2017 and is expected to reach 233.56 billion tons by 2022, at a CAGR of 6.1% from 2017 to 2022.
- Climate Change & Climatology
- Evidence of Climate Changes
- Biodiversity Scenarios
- Carbon Cycle
- CO2 Capture and Sequestration
- Climate Hazards
- Risks of Climate Change
- Energy Policy
Track 11-Bioremediation:

Bioremediation is becoming the technology of choice for the remediation of many contaminated environments, particularly sites contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons. Bioremediation stimulates the growth of certain microbes that use contaminants as a source of food and energy.
It is very important to understand that this form of waste remediation uses no toxic chemicals, although it may use an organism that can be harmful under certain circumstances. A gross, but simple explanation of bioremediation is the use of maggots in wound care control. Wounds that have contamination can have maggots introduced to them. The maggots then eat the contamination, allowing the wound to heal correctly. That is a form of medical bioremediation but there are many other types that are used to control different waste contamination.
The worldwide marketplace for bioremediation technology & services marketplace changed into worth USD 32.2 billion in 2016 and is expected to reach USD 65.7 billion by using 2025 at a CAGR of 8.3% from 2017 to 2025.
- The Roles of Microbes in Bioremediation
- Variation in Basic Metabolism
- Nutritional Requirements for Contaminant Destruction
- Indicators of Microbial Activity
- Complicating Factors
Track 12-Waste Treatment Technologies:
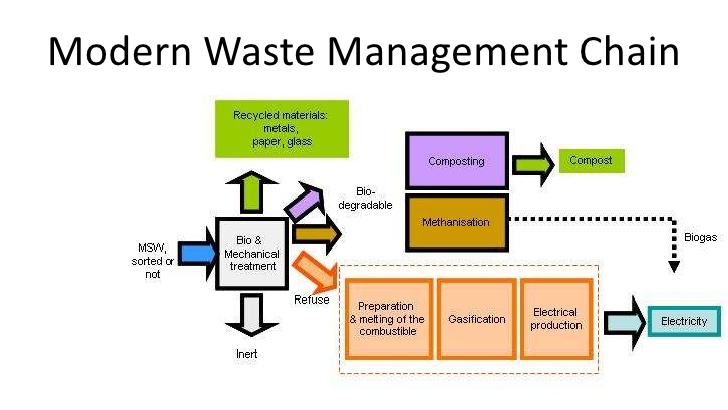
There are a number of different waste treatment technologies for the disposal, recycling, storage, or energy recovery from different waste types. Each type has its own associated of waste Management. Relatively simple waste treatment technologies can be designed to provide low cost sanitation and environmental protection while providing additional benefits from the reuse of resources. These technologies use natural aquatic and terrestrial systems Composition and generation.
The demand for water and wastewater treatment (WWT) products in the top 40 national markets was $47.7 billion in 2012. This total market is expected to reach nearly $53.1 billion in 2013, $59.2 billion in 2014 and about $96.3 billion by 2019, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.2% for the period of 2014 to 2019.
- Pyrolysis
- Incineration
- Ion Exchange
- Advanced Oxidation Processes
- Membrane Filtration
- Gasification
- Mechanical Biological Treatment
Track 13-Bio- Energy from waste:

The potential for increasing total traditional biomass utilization for energy purposes is limited. The thrust of the activities is therefore twofold, one aim is to broaden the scope of biomass utilization into upgrading and the other aim is to broaden the biofuel base as such. This in turn implies an enhanced focus on fuels for transportation and power generation with respect to traditional biomass and a focus on direct heating for more complex biomass, such as waste etc.
The worldwide waste to electricity (WTE) marketplace size turned into USD 25.0 billion in 2015 and is predicted to witness a sizable increase over the forecast length. Increasing demand for renewable assets is anticipated to propel the global waste to electricity market over the forecast duration. A shift in awareness closer to substitutes along with coal with renewable assets to reduce carbon content is likewise projected to play an essential position in shaping the enterprise.
- Biodiesel
- Biofuels
- Biomass Fraction
- Gasification
- Bio-Oil Upgrading
- Thermo-Chemical Conversion
Track 14-Environmental Impact Assessment:

The purpose of Environmental Impact Assessment is to rectify and evaluate the potential impacts of development and projects on the environmental system. It is a useful aid for decision making based on understanding of the environment implications including social, cultural and aesthetic concerns which could be integrated with the analysis of the project costs and benefits.
According to figures compiled by EA, the EIA and sustainable development consultancy work area was worth just shy of £250 million in 2013, which is some 44% higher than where it was at the height of the recession in 2010. Demand for these services has been growing since 2011 as the government prioritised infrastructure investment as a means of stimulating economic growth.
- Environmental Indicator
- Natural Landscape
- Strategic Environmental Assessment
- Economic and Demographic Factors
- Conversation of Biodiversity
Track 15-Landfills:

A landfill is a carefully constructed and monitored structure that isolates trash from the surrounding environment. This isolation is accomplished with the use of a bottom liner and daily covering of soil. Landfills can create energy. Landfills need expert design as well as professional operators and a proper management to guarantee their functionality.
Americans annually generate approximately 258 million heaps of MSW of which about 53% is deposited in landfills, a percentage that has plateaued in latest years. Currently, 35% of MSW is recycled and 13% is combusted for power production. There's a need to change the way we think about how strong waste is generated, managed, and probably used as a useful resource. We need to recognize that what is automatically discarded can also, in truth, be a reusable aid.
- Plasma Arc Gasification
- Waste Disposal
- Landfill Diversion
- Secure Landfills
- Landfill Gas
- Landfill Fires
Track 16-Waste Processing Industries:

The progressive development of the waste processing industry derives directly from the rapid progress in packaging industry. In addition to the inevitable scrap or reject production loads of in-process waste is produced in packaging industry.
Coupled with rapid industrialization and shifting of industries in different regions toward Asia-Pacific, the location has witnessed exponential growth in industrial sports, ensuing in massive quantities of generated industrial waste. This widespread amount of generated waste requires powerful processing and disposal to limit environmental hazards. However, as current commercial waste processing systems are grossly inadequate, the place is anticipated to witness massive investments in the waste recycling and services industry. The commercial waste management market in Asia-Pacific is anticipated to develop at a CAGR of 11.4% between 2014 and 2019.
- Hazardous Wastes
- Carcinogenic
- Chemical Waste
- Biomedical Waste
Track 17-High Performance & Green Buildings:

High-performance buildings reflect design excellence. These buildings--often also referred to as "green" or "sustainable"--minimize environmental impact and produce cost savings over their life cycle. These buildings are best designed in an integrative fashion wherein owners, designers and contractors commit from the onset to work together and follow high-performance building principles when addressing critical issues.
The survey shows that global green building interest keeps doubling every three years. Extra people apprehend the monetary and manufacturing value that green homes carry to assets proprietors and tenants, along with the energy and water blessings to the surroundings, that's using the green building industry’s growth. It’s a win-win for people, planet and the economy.
- New Construction vs. Adaptive Reuse
- Site Selection, Planning and Design
- Energy- and Water-Efficiency
- Use of Renewable Energy
- Indoor Environmental Quality
- Efficient and Environmentally Friendly Materials
- Recycling During and After Construction
- Building Commissioning
Track 18-Trends in Energy Efficiency:

Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the goal to reduce the amount of energy required to provide products and services. Energy efficiency has to be increased at all stages of the energy chain, from generation to final consumption. At the same time, the benefits of energy efficiency must outweigh the costs, for instance those that result from carrying out renovations.
Global energy efficiency has seen positive signs across developed and developing countries. This has resulted in energy savings of 450 million of oil equivalent in 2015. If this can be put in a simpler perspective, the quantity of energy saved could power the whole of Japan for a year. These savings also resulted in reduction of total energy expenditure by $540 billion, another startling fact.
- Smart Cities, Cities That Run Themselves
- Distributed Generation in Smart Cities
- The Electric Vehicle, a Reality Today
- Electric Energy Management from Mobile
- Big Data, the Classic "Information Is Power"
Track 19-Energy Storage:

Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time. A device that stores energy is sometimes called an accumulator or battery. Energy comes in multiple forms including radiation, chemical, gravitational potential, electrical potential, electricity, elevated temperature, latent heat and kinetic. Energy storage involves converting energy from forms that are difficult to store to more conveniently or economically storable forms. Bulk energy storage is currently dominated by hydroelectric dams, both conventional as well as pumped.
In 2017, Germany invested nearly 80,000 commercial and household operations inside the PV-battery device. Studying the market assessment, the United States is anticipated to install 50,000 extra PV-battery devices annually, by using 2020. The increasing demand for solar PV is envisioned to increase in response to de-carbonization and declining device value of the power quarter across the globe. For this reason, the strength garage market is expected to be majorly driven via the growing solar power marketplace.
- Fossil Fuel Storage
- Mechanical
- Electrical, Electromagnetic
- Biological
- Electrochemical (Battery Energy Storage System, BESS)
- Thermal
- Chemical
Track 20-Strategies to Control Environmental Damage:
Many environmentalist and scientist are working to make certain strategies to reduce environmental pollution. In addition to solid waste which we see in our household garbage bins, there are medical, industrial, agricultural and mining wastes. Environment is polluted mostly by improper disposal of waste. Therefore there is a need to keep a check over waste disposal.
Environmental problems are so diverse and diffused that virtually any activity of civilization interacts with the environment. Many environmental pollution problems are local in character and they can be controlled by creating environmental consciousness in each and every citizen. People should be told about the importance of clean atmosphere as well as about the consequences of different types of environmental pollutions. Besides, action is also needed at national level and guidelines may be established internationally by the United Nations Joint Committee of Experts.
- Recycling
- Sewage Treatment
- Green Chemistry
- Basic Aims of Green Chemistry
- Anaerobic Septic Tank Treatment
Track 21-Green Power:

Green energy comes from natural sources like wind, water, and sunlight. It is much more environmentally friendly than other types of energy and doesn’t contribute to climate change or global warming. Unlike fossil fuels, green energy sources replenish naturally and are in continuous supply.
The maximum recent update, repute and tendencies inside the U.S. Voluntary green strength marketplace, released in 2017, unearths that about 6.3 million customers procured approximately 95 million megawatt-hours (MWh) of green power in 2016, which represents a 45% increase in the variety of clients and a 19% growth in the quantity income from 2015. The voluntary green power market now accounts for about 28% of all U.S. renewable power income, except massive hydropower.
- Solar
- Wind
- Geothermal
- Biogas
- Edible Biomass
- Hydroelectric Sources
Track 22-Water Conservation Program:

Water conservation includes all the policies, strategies and activities to sustainably manage the natural resource of fresh water, to protect the hydrosphere, and to meet the current and future human demand. Population, household size, and growth and affluence all affect how much water is used. Factors such as climate change have increased pressures on natural water resources especially in manufacturing and agricultural irrigation.
The New York town water delivery system is an incorporated network of 19 reservoirs and 3 managed lakes. The system gives you approximately a billion gallons of water per day to over 8 million users. With the city’s populace predicted to upward thrust to 9.1 million by using 2030, conservation will hold to have a critical function in assembly needs for water. It’s far crucial to be aware that although populace boom has multiplied the call for housing, electricity, and transportation, overall water intake has been declining and is lower today than it became 50 years in the past.
- Rainwater Harvesting
- Habitat Conservation
- Fresh Water
- Water Utilities
- Irrigation
Track 23-Alternate Water Resources:

Alternative water is often treated to non-potable standards, meaning it is not safe for human consumption. Common uses of alternative water include landscape irrigation, ornamental pond and fountain filling, cooling tower make-up, and toilet and urinal flushing.
Water shortages have already been faced within the examine place because of droughts, and that they had been conquer by using managing call for. The discount in Israeli water use from 1,987 million m3/year in 1987 to one, 420 million m3/yr in 1991 without an internet loss in agricultural manufacturing or monetary boom indicates what can be completed inside the way of demand moderation.
- Harvested Rainwater from Roofs
- Onsite Storm Water
- Grey Water
- Discharged Water from Water Purification Processes
- On-Site Reclaimed Wastewater
- Captured Condensate from Air Handling Units.
Track 24-Environment Legislation:

Environmental legislation is the collection of laws and regulations pertaining to air quality, water quality, the wilderness, endangered wildlife and other environmental factors. The umbrella of environmental legislation covers many laws and regulations, yet they all work together toward a common goal, which is regulating the interaction between man and the natural world to reduce threats to the environment and increase public health.
In India, the National Environment Policy (NEP), 2006 was made by the Ministry of Environment and Forests to view the key environmental challenges, their causes and effects, objectives of policy formulation and strategies and action programme to satisfy the objectives and mechanisms that need to be implemented and reviewed.
- Water Quality
- Waste Management
- Contaminant Clean-up
- Chemical Safety
- Trans-boundary Responsibility
- Public Participation and Transparency
- Precautionary Principle
- Prevention
- Polluter Pays Principle
LEARN MORE
Top Waste Management and Environmental Science Universities Worldwide:
Top Waste Management and Environmental Science Related Universities in Europe:
South-Eastern Finland University of Applied Sciences, Finland | Tallinn University of Technology,Estonia | Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, Russia | Politecnico di Milano, Italy | Kaunas University of Technology, Lithuania | University of Central Lancashire, England | University of Central Lancashire, England | Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, Russia | Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, Russia | University of Pavia, Italy | Aalto University, Finland | University of Glasgow, Scotland | RWTH International Academy, Germany | Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, Russia | Budapest University of Technology and Economics (BME), Hungary | Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, Russia | VHL University of Applied Sciences, Netherlands | University of Glasgow, Scotland | University of Debrecen, Hungary | Teesside University, United Kingdom | University Carlos III of Madrid, Spain | University of Central Lancashire, England | Linköping University, Sweden | University of Central Lancashire, England | University of Central Lancashire, England | Mälardalen University, Sweden | Iuss Institute For Advanced Study, Pavia, Italy | University of Central Lancashire, England | Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden | Aalto University, Finland | Tallinn University of Technology, Estonia | Linnaeus University, Sweden | Centrale Nantes, France | Teesside University, United Kingdom | Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden | Linnaeus University, Sweden | Delft University of Technology, Netherlands | Szent István University, Hungary | University of Debrecen, Hungary | Ca' Foscari University of Venice, Italy | Centrale Nantes, France
Top Waste Management and Environmental Science Universities in The U.S.A:
University of California—Berkeley, CA| University of Illinois—Urbana-Champaign, IL| Stanford University, CA | University of Michigan , MI | University of Texas—Austin, TX | Virginia Tech, VA | Georgia Institute of Technology , GA | Carnegie Mellon University , PA | University of Colorado, CO| Massachusetts Institute of Technology, MA | Yale University, CT
Top Environmental Science And Engineering Universities In Asia:
University of Tokyo, Japan | Kyushu University,Japan | Nagoya University,Japan | National University of Singapore,Singapore | Ngee Ann Polytechnic,Singapore | University of science and technology Beijing,china | graduate school at Shenzhen Tsinghua university,China | Shanghai Jiao Tong University,China | Zhejiang University,China | Huazhong University of Science and Technology,China | Sichuan University,China
Environmental Science And Engineering Conferences Worldwide:
International Conference on Civil and Environmental Engineering, Germany | International Conference on Food and Environmental Sciences, Vietnam | International Conference on Environment and Renewable Energy, Vietnam | International Conference on Environmental Sustainability, Development and Protection, Hungary | International Conference on Civil and Environmental Engineering , Austria | International Convention On Geochemistry And Environmental Chemistry , Canada | International Conference On Geological And Environmental Sustainability, Indonesia | International Conference on Sustainability, Human Geography and Environment 2018 , Poland | Ecolgy Ecosystems 2018, Canada | Climate 2018, USA | Marine Science 2018, USA | Global Warming 2018, Canada | Recycling Expo-2018, Germany | Green Energy Congress 2018, UK | Climate Change 2018, UK | Recycling Congress 2018, Netherlands | Bio-diversity Con gress-2018, Australia | Natural Hazards Congress-2018, Australia | Recycling Summit 2018, Japan | Environment and Health Congress 2018, Australia
Top Environmental Science And Engineering Journals Worldwide:
Bioresource Technology | Building and Environment | Coastal Engineering | Environmental Modelling and Software | Journal of Hazardous Materials | Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology | Science of the Total Environment | Reviews in Environmental Science and Biotechnology | Agronomy for Sustainable Development | Indoor Air | Ocean Engineering | Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment | Journal of Environmental Management | Ecological Engineering | Journal of Environmental Quality | AICHE Journal | International Journal of Marine Energy | International Journal of Sustainable Transportation | Journal of Environmental Sciences | Environmental Processes | Biodegradation | Environmental Geochemistry and Health | Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy | Process Safety and Environmental Protection: Transactions of the Institution of Chemical Engineers, Part B | Journal of Flood Risk Management | Waste Management and Research | Engineering in Life Sciences | Journal of Hydro-Environment Research | Sustainable Production and Consumption | Science and Technology for the Built Environment | Water, Air, and Soil Pollution | International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology | Journal of Polymers and the Environment | Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology | Environmental Progress and Sustainable Energy | Journal of Environmental Science and Health - Part A Toxic/Hazardous Substances and Environmental Engineering | Environment | Greenhouse Gases: Science and Technology | Paddy and Water Environment | Waste and Biomass Valorization | Journal of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics | Bio Resources | International Journal of Energy and Environmental Engineering | Journal of Environmental health science and Engineering | Journal of biological engineering | Asian Journal of Plant Science & Research | Journal of Petroleum & Environmental Biotechnology | Journal of Bioremediation & Biodegradation | Advances in Applied Science Research
Top Environmental Science And Engineering Companies Worldwide:
National Grid | Golder Associates | Genesis Oil and Gas | Peter Brett Associates | Atomic Weapons Establishment | PWS Technical Services Limited | Ander elite | Fair Hurst | Human Capital Solutions | TSP Projects | QinetiQ | BAE Systems | Unilever | Frontier Agriculture Ltd | Thales | Group Lotus | Kier Group | Black & Veatch | SOCOTEC UK Limited | Atkins | WSP | Fairmont St Andrews | WYG Group Ltd | AECOM | Morgan Sindall Plc | STANTEC INC. | CDM SMITH | LEIDOS
Application Of Environmental Science & Engineering:
Drinking water and waste water treatment | Strong waste administration | Unsafe Substance Treatment and Control | Air Quality Management | Normal assets administration | Ecological arrangement and direction improvement | Natural effect appraisal and alleviation | Polluted asset administration or site remediation
Environmental and Waste Management Keywords:
Eco-Science | Climate Change | Natural Resources | Pollution | Green Science | Global Warming | Renewable Sources Of Energy | Non-Renewable Sources Of Energy | Earth Science | Environmental Issues | Recycling | Sustainability | Carbon dioxide | Free Energy | Waste Management | Pollution Control | Deforestation | Earth Science | Natural Resources | Environmental Laws | Ecosystem| Greenhouse Effect | Environmental Agency | Wind Energy | Solar Energy | Geothermal Energy | Air Pollution | Water Pollution | Land Pollution | Noise Pollution | Environmental Biotechnology | Hazardous Waste | Ozone | Pollutant | Smoke | Smog | Waste Water Treatment | Toxicity | Toxic Substance | Waste Recycling and Reuse | Coastal Zones and Oceanography | Green Energy | Environmental Pollution | Ecology and Ecosystems | Environmental Toxicology | Green Chemistry | Green Engineering | Sustainable Environment | Pollution Control | Natural Hazards | Disaster Management | Biodiversity Conservation | Ecosystem Management | Coastal Dynamics and Management | Water Resource Management | Environmental Chemistry | Biosphere | Landscape Conservation | Environmental Genomics | Special Ecology | Restoration Ecology | Industrial Pollution | Pollution Sources | Bioenergy | Biofuels | Bio-Degradable | Non Bio-Degradable | stratosphere | Habitat | Ground Water | Bio-accumulation | Biosphere | Conservation Of Nature | Energy Conservation | Sustainable Development | World Environment Day | Geo-Science | Atmospheric Science














